Pump Specific speed is a dimensionless number used in design. Specific speed is used to find out the geometry of the impellers and it is helpful in identifying the type of impeller to be selected for particular application.
Formula for Calculation of Pump Specific Speed
Specific speed of the pump is calculated with the help of the formula:
Ns = (N * √Q )/ H(3/4)
Where
Ns is Specific speed of the pump Dimensionless
N is Speed of the pump in rpm
Q is the Volume Flow rate of the pump at its best efficiency point – BEP in gpm
H is Discharge head of the pump at BEP in ft
In SI units the formula can be used as
Ns = (N * √Q)/ (1.16 * H (3/4) )
Where
Ns is Specific speed of the pump Dimensionless
N is Speed of the pump in rpm
Q is the Volume Flow rate of the pump at its best efficiency point – BEP in m3/hr
H is Discharge head of the pump at BEP in m
Note:
While calculating specific speed use flow rate and discharge head at its best efficiency point.
For Double suction pumps use half of the volume flow rate at BEP while calculating specific speed.
Per stage pump head to be used in calculations.
Application of Pump Specific Speed
Based on suction specific speed impellers are selected from the following three types
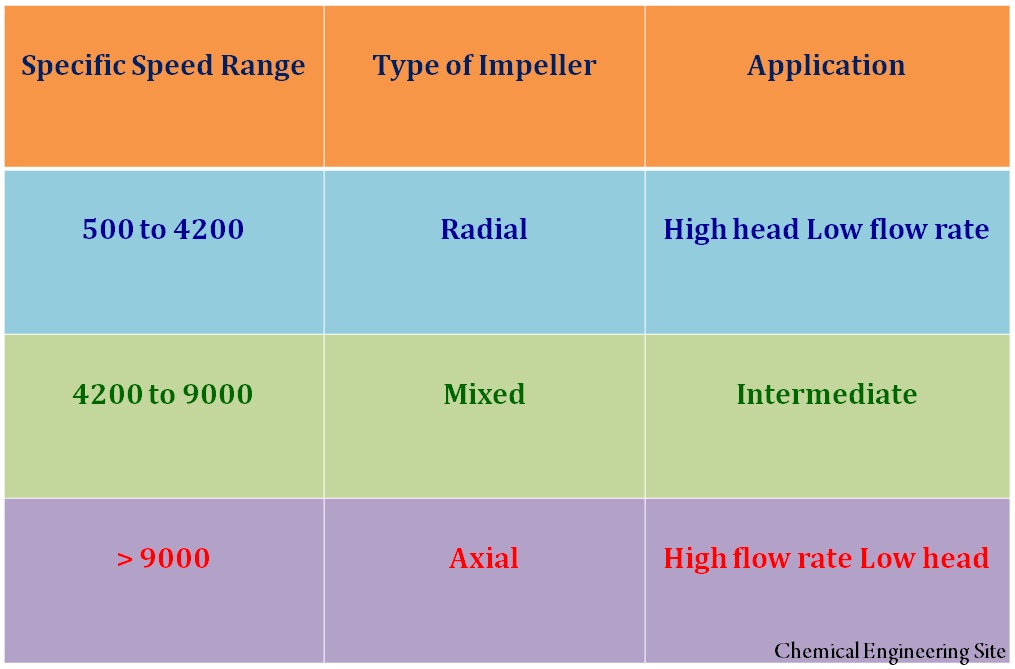
Radial Flow Impellers
In radial flow type impellers fluid leaves perpendicular to the pump shaft center line giving high head and low flow rate. Radial flow impellers develop head with centrifugal action. Radial flow type of impeller is selected when the pump specific speed is between 500 to 4200.
Axial Flow Impellers
In axial flow type impellers fluid enters and leaves along the same direction parallel to the rotating shaft centerline giving high flow rate and low head. Axial Flow type of impeller is selected when the specific speed is greater than 9000
Mixed Flow Impellers
In Mixed flow type impellers fluid leaves at an angle below 45 degree from the shaft center line. In mixed flow design, part of head is developed by centrifugal action and part of head is developed by impeller design. Mixed flow type of impeller is selected when the pump specific speed falls between 4200 to 9000.
Find it Interesting? Learn more about Centrifugal Pump in our website and Dont miss our Pump Quiz
Buy Related Books:
PERRY’S CHEMICAL ENGINEERS’ HANDBOOK,8/ED from Flipkart.com