Centrifugal pump Affinity laws are set of mathematical equations correlating the Flow Rate, Head, Brake Horse Power, Speed and Impeller Diameter of the pump. Pump efficiency is considered as a constant and variation in speed and impeller diameter is analyzed for the variation in above said parameters. Using the new set of data derived from pump affinity laws a new set of pump characteristic curve may be formulated and can be used.
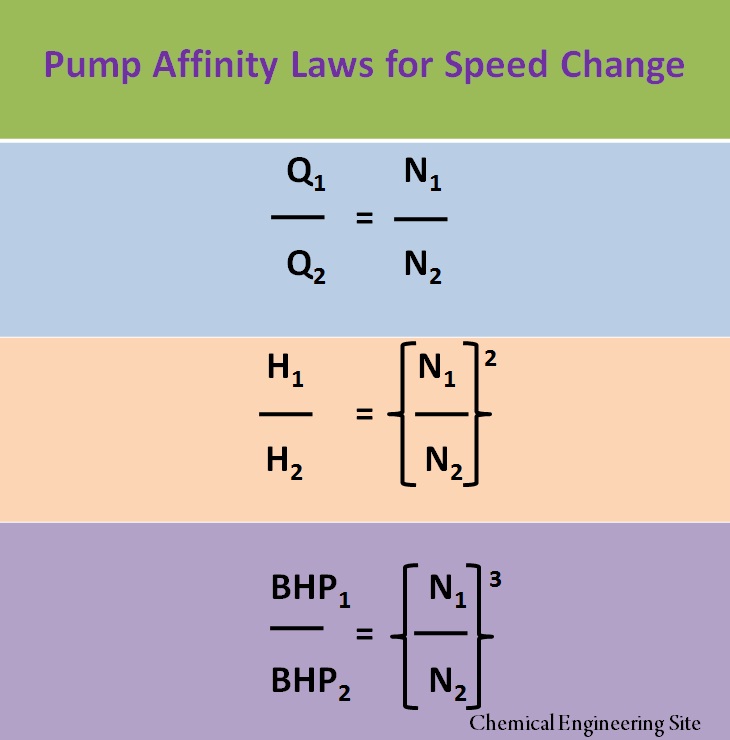
Pump Affinity Laws
Q1 / Q2 = N1 / N2
Flow Changes directly to the change in Speed
H1 / H2 = (N1 / N2)2
Head Changes directly proportional to the Square of the change in Speed
BHP1 / BHP2 = (N1/ N2)3
Brake Horse Power Changes directly proportional to the Cube of the change in Speed
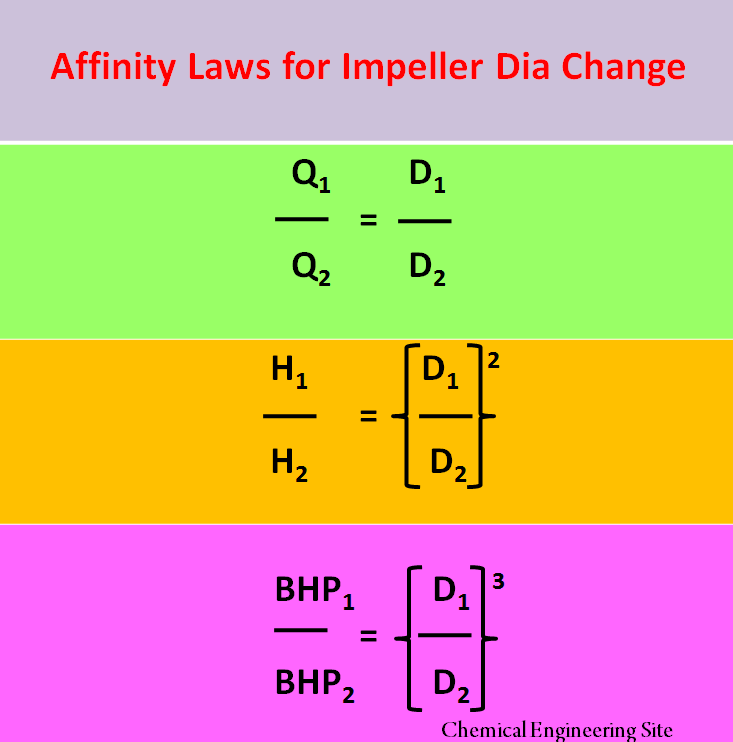
For a fixed speed and varying impeller diameter pump affinity laws are as follows:
Q1 / Q2 = D1 / D2
H1 / H2 = (D1 / D2)2
BHP1 / BHP2 = (D1 / D2)3
Nomenclature:
Q1, Q2 – Volumetric Flow rate in m3/hr
H1, H2 – Head in m
D1, D2 – Diameter of the impeller in mm
N1, N2 – Speed in rpm
BHP – Brake Horse Power in kW
The above two cost reduction techniques in Centrifugal pump may be analyzed using the Pump Affinity Laws before implementation of the project.
Pump Affinity Laws Calculator in Excel
To help the process engineers in Chemical Processing Industry, Pump Affinity laws are incorporated in Excel file and uploaded. You may download this template and use it for Pump Affinity law Calculations.
Excel Calculation File Available Here
Application of Pump Affinity Laws
The practical application of Centrifugal Pump Affinity laws is helpful in implementing energy savings in oversized pumps. In an industry process related pumps may be over sized because of various reasons or it may be underutilized based on the required operating conditions. This results in waste of energy. Pump affinity laws are helpful in implementing “VFD” and “Impeller Trim”.
Variable Frequency Drives are installed for the motor to vary the pump speed according to the requirement and it reduced power requirement.
“Impeller Trim” operation is carried out to reduce the impeller diameter of the pump to reduce the power consumption.
Learned something? It might be interesting to test your knowledge on Pumps in our Pump Quiz module.
Get unlimited access to 5,000+ magazines, newspapers and curated premium stories at flat 55% off