What is Flash Steam?
Flash Steam is the steam formed whenever hot condensate at high pressure and temperature is allowed to drop into a low pressure side. It is formed by boiling of the condensate which contains more heat than it can hold at that low pressure.
Most Common Sources of Flash Steam recovery in a Chemical Process Industry includes Blow Down from Boilers and Condensate from Steam traps.
Blow Down from Boilers
Continuous and Intermittent Blow down in Boilers is given to control the Silica and Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) Levels in Circulating Boiler feed water. Normally this Blow down water is available at High Pressure and its corresponding saturation Temperature as most of the Boilers in Chemical Process Industries operate at high pressure. Blow down boiler feed water contains enough heat to produce flash steam and the condensate can be reused again.
Condensate from Steam traps
Steam Traps are widely employed in Steam distribution network to discharge the condensate from the steam lines as soon as it is formed. This prevents two phase flow in steam lines enabling us in reducing the pressure drop and increasing the life of the pipelines preventing water hammer. The hot condensate from the steam traps is also at variable pressure depending on the Process Design of the steam system of the particular industry. The heat in the condensate can also be effectively utilized to produce flash steam from it.
Flash Steam Calculation
Formula for calculating the flash steam generated is given below.
Percentage of Flash Steam Generated = (Hf1– Hf2)/Hfg2 * 100
Hf1: Liquid Enthalpy at Initial Pressure in kJ/kg
Hf2: Liquid Enthalpy at Final Pressure in kJ/kg
Hfg2: Enthalpy of Evaporation at Final Pressure in kJ/kg
Quantity of Flash Seam = % of Flash Steam Generated * Quantity of Condensate
Calculation of Flash Steam
Boiler Blow down condensate is available at 100 bar g. It is allowed in a flash steam recovery vessel which operates at 10 bar g. If the blow down rate is at 4 TPH.
Calculate the following
1. Percentage of Flashing
2. Quantity of Flash Steam Produced
3. Quantity of Condensate generated
Solution:
From Steam tables,
Liquid Enthalpy at Initial Pressure 100 bar in kJ/kg = 1411.68
Liquid Enthalpy at Final Pressure 10 bar in kJ/kg = 781.656
Enthalpy of Evaporation at Final Pressure 10 bar in kJ/kg = 1999.67
Saturation Temperature at 100 bar = 311.772 Deg C
Saturation Temperature at 10 bar = 184.154 Deg C
From the above values it is clear that at 100 bar the saturation temperature is 311 Deg C and at 10 bar it is 184 Deg C. This excess heat is used for converting the part of the condensate into steam and it is called as flash steam or secondary steam.
Percentage of Flash Steam Generated = (Hf1– Hf2)/Hfg2 * 100
= (1411.68-781.656)/1999.67 * 100
Percentage of Flashing = 31.50 %
Quantity of Flash Seam = % of Flash Steam Generated * Quantity of Condensate
= 31.50 /100 * 4 TPH
= 1.26 TPH
Quantity of Condensate generated = Quantity of Condensate In – Quantity of Flash Seam Generated
= 4 – 1.26
= 2.73 TPH
Control System for Flash Steam
The main control systems employed in Flash steam recovery system are Pressure control and Level control. We shall see them in detail.
Pressure Control
Pressure control in the flash steam recovery vessel is very important. The flash steam generated may directly send to a steam system which is already present in the Process Plant. Otherwise a separate pressure control valve has to be introduced in the Steam pipeline to control the flash steam recovery vessel. The pressure fluctuation may be persisting due to variation in condensate inlet from the boiler and steam traps. Therefore pressure control system is necessary.
Level Control
The level in the flash steam vessel is controlled with the help of a level control valve located in the condensate outlet line. In case of flash vessel operating at atmospheric pressure overflow drains may be provided to control the level in the vessel.
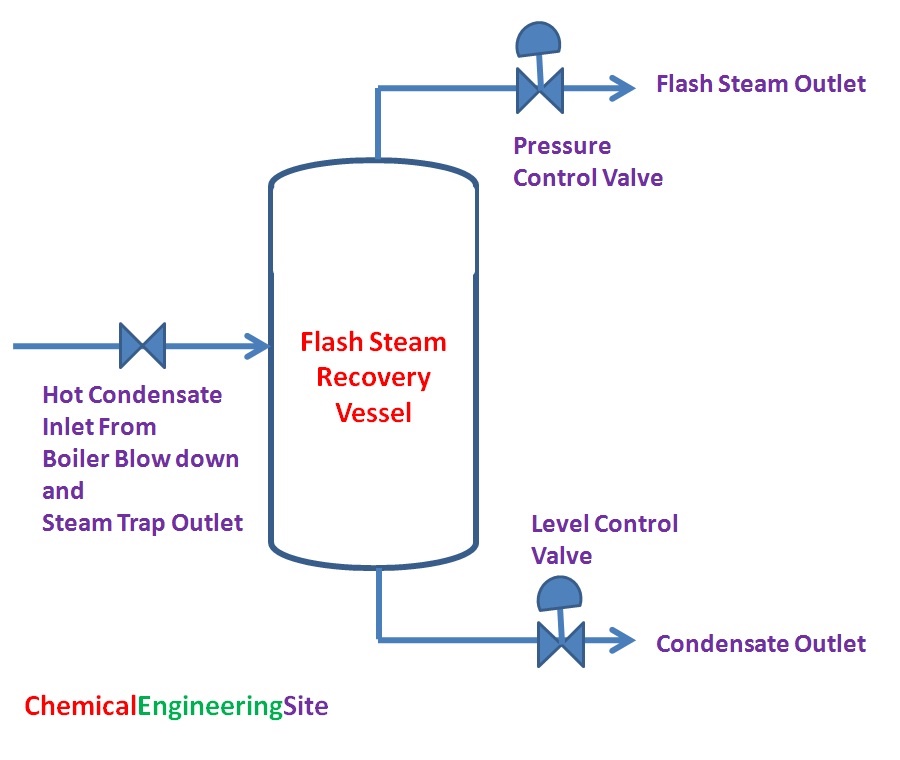
Other Piping
Feed Inlet Non Return Valve (NRV) -To avoid condensate backup from other inlet headers. Eg Boiler Blow down should not go into Steam trap condensate.
Flash Steam Outlet NRV – To avoid Steam backup from steam header
Vessel Relief Valve – To prevent overpressure in case of Pressure or level control valve failure
Flash Steam Calculation Tools
In calculation of flash steam it is important to have the properties of steam and water at various pressures. This can be obtained from steam tables. Steam Table application for computer and Laptops is available here. This is a free application useful in determining Properties of Saturated Liquid and Vapor states of water.
Android Steam Table Application is the free tool for Android Mobile Phones. This helps in calculating Saturated Properties by Pressure and Temperature which is useful for calculating flash steam recovery calculations. This free App can be downloaded here
For Calculating the Properties of saturated steam and water online this website can be used.
Buy Related Books:
Steam Tables With Mollier Diagram from Flipkart.com